The rise of hybrid workspaces and the role of structured cabling
The world of work has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years, with hybrid workspaces becoming a cornerstone of the modern workplace. This shift—driven by technological advancements, changing employee expectations, and the global disruption of traditional work norms—has created a model that seamlessly blends in-office and remote work. Structured cabling, the invisible infrastructure that powers connectivity and productivity in hybrid workspaces is at the heart of this evolution.
The shift to hybrid workspaces
In hybrid workspaces, connectivity is king. Employees must be able to collaborate across locations without interruptions, whether they’re participating in virtual meetings, accessing cloud-based tools, or sharing large files. Poor connectivity not only disrupts productivity but can also erode employee morale and engagement. This is where structured cabling systems come into play.
These systems form the backbone of hybrid workspaces, enabling reliable and high-speed data transmission that supports the diverse technologies in use today.
The importance of connectivity
What is structured cabling?
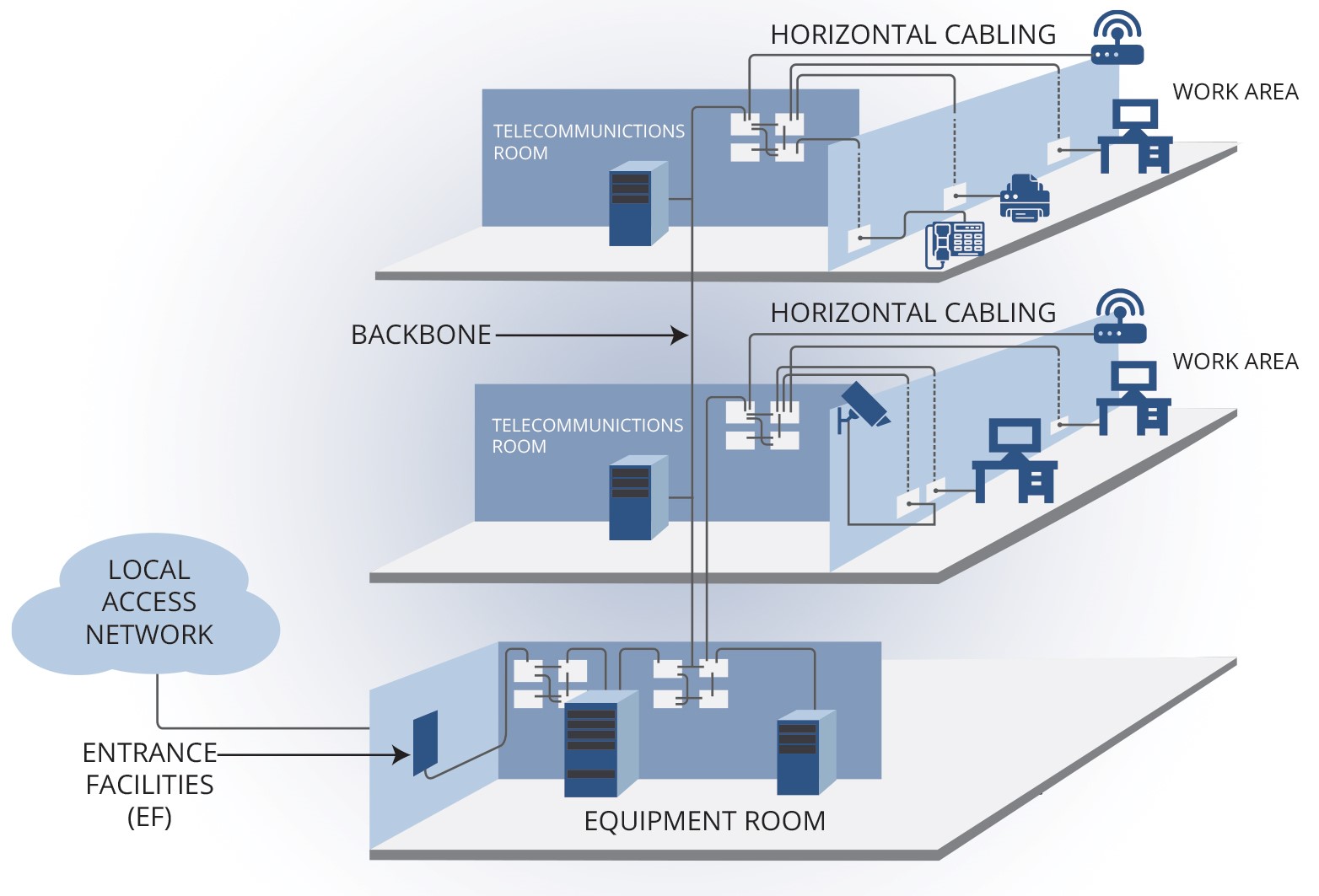
Structured cabling is an organized approach to laying out and managing a building’s telecommunications and data network. Unlike ad-hoc wiring, structured cabling adheres to standardized specifications and best practices, ensuring a scalable, flexible, and efficient network infrastructure. It includes various subsystems, such as:
Horizontal Cabling: Connects workstations to telecommunication rooms.
Backbone Cabling: Links different floors or buildings within a campus.
Telecommunications Room: Houses equipment like patch panels and switches.
Work Area Components: Includes cables and connectors at the workstation.
How structured cabling supports hybrid workspaces
Seamless collaboration
- Hybrid workspaces rely heavily on collaboration tools, such as video conferencing platforms, shared drives, and instant messaging apps. Structured cabling ensures that these tools function without lag or connectivity issues, even during peak usage times. With high-speed data transmission capabilities, employees can collaborate effortlessly, regardless of their location.
Scalability for future growth
- Hybrid work models often involve fluctuations in workforce size and technology requirements. Structured cabling provides the flexibility to scale up or down as needed, accommodating additional devices, new technologies, or increased bandwidth demands without requiring a complete overhaul of the network.
Enhanced reliability
- Redundancy and reliability are critical in hybrid work environments. Structured cabling systems are designed to minimize downtime by reducing the risk of tangled or damaged cables. With proper planning and installation, businesses can achieve a robust network that supports uninterrupted operations.
Support for IoT devices
- Hybrid offices often integrate Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart lighting, climate control systems, and access control solutions. Structured cabling enables these devices to communicate efficiently, creating a seamless, automated workspace that enhances comfort and productivity.
Improved security
- Hybrid workspaces require secure networks to protect sensitive data. Structured cabling supports advanced security measures, such as VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and firewalls, by providing a stable and organized foundation for these technologies.
Cost efficiency
- Although structured cabling requires an upfront investment, it reduces long-term costs by simplifying maintenance and minimizing the need for repairs or upgrades. Its modular design allows for quick modifications, saving time and resources when adapting to new business needs.
Key considerations when implementing structured cabling
Assessing current and future needs
Before installation, organizations should assess their current technology requirements and anticipate future needs. This includes evaluating the number of employees, types of devices, and bandwidth demands to ensure the cabling system is designed for scalability.
Compliance with standards
Adhering to industry standards, such as ANSI/TIA-568, ensures that the cabling system is reliable, interoperable, and compatible with a wide range of equipment.
Choosing the right cabling type
Different types of cables, such as Cat.5e, Cat.6, and fiber optics, offer varying levels of performance. The choice depends on factors like data transfer speeds, distance, and budget.
Professional installation and maintenance
Structured cabling systems must be installed by certified professionals who understand the complexities of network design. Regular maintenance and audits are also essential to identify and resolve potential issues before they impact operations.
The role of structured cabling in emerging technologies
The hybrid work model is closely tied to advancements in technology, such as 5G, edge computing, and AI-driven analytics. Structured cabling serves as the foundation for these innovations, enabling businesses to adopt them seamlessly.
5G and Wi-Fi 6: These technologies promise faster wireless connectivity, but they still rely on robust wired networks to support backhaul data transmission. Structured cabling ensures that 5G and Wi-Fi 6 networks operate efficiently.
Cloud computing: As hybrid workspaces depend on cloud-based tools, structured cabling facilitates the high-speed connectivity needed for smooth cloud access.
Edge computing: By supporting localized data processing, structured cabling enhances the performance of edge computing applications, which are critical for latency-sensitive tasks in hybrid environments.
Looking ahead: The future of hybrid workspaces
As hybrid workspaces continue to evolve, the role of structured cabling will become even more critical. Emerging trends, such as smart office automation, virtual reality (VR) collaboration, and AI-driven workplace analytics, will demand robust and scalable network infrastructures. Businesses that invest in structured cabling today will not only enhance their current operations but also position themselves to adapt to future technological advancements. This infrastructure ensures that hybrid workspaces remain flexible, productive, and resilient in the face of ongoing change.








